Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP) is a uncommon autosomal dominant dysfunction characterised by congenital malformation of the nice toes and by progressive heterotopic bone formation in muscle tissue. Recently, a mutation involving a single amino acid substitution in a bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) kind I receptor, ALK2, was recognized in sufferers with FOP.
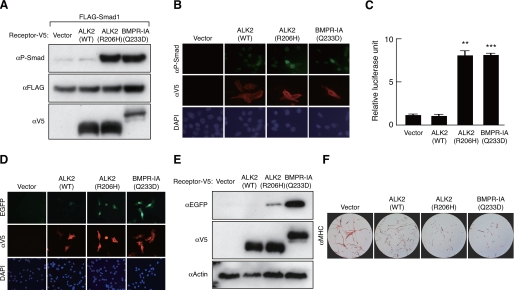
We report right here that the similar mutation, R206H, was noticed in 19 Japanese sufferers with sporadic FOP. This mutant receptor, ALK2(R206H), prompts BMP signaling with out ligand binding. Moreover, expression of Smad1 and Smad5 was up-regulated in response to muscular harm.
ALK2(R206H) with Smad1 or Smad5 induced osteoblastic differentiation that may very well be inhibited by Smad7 or dorsomorphin. Taken collectively, these findings recommend that the heterotopic bone formation in FOP could also be induced by a constitutively activated BMP receptor signaling by way of Smad1 or Smad5.
Gene switch of Smad7 or inhibition of kind I receptors with dorsomorphin could symbolize methods for blocking the exercise induced by ALK2(R206H) in FOP.
Smad6 is a Smad1/5-induced smad inhibitor. Characterization of bone morphogenetic protein-responsive factor in the mouse Smad6 promoter.
Smad6 is an inhibitory Smad that’s induced by bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) and interferes with BMP signaling. We have remoted the mouse Smad6 promoter and recognized the areas chargeable for transcriptional activation by BMPs.
The proximal BMP-responsive factor (PBE) in the Smad6 promoter is necessary for the transcriptional activation by BMPs and comprises a 28-base pair GC-rich sequence together with 4 overlapping copies of the GCCGnCGC-like motif, which is a binding website for Drosophila Mad and Medea.
We generated a luciferase reporter assemble (3GC2-Lux) containing three repeats of the GC-rich sequence derived from the PBE. BMPs and BMP receptors induced transcriptional activation of 3GC2-Lux in varied cell sorts, and this activation was enhanced by cotransfection of BMP-responsive Smads, i.e.
Smad1 or Smad5. Moreover, direct DNA binding of BMP-responsive Smads and common-partner Smadfour to the GC-rich sequence of PBE was noticed. These outcomes point out that the expression of Smad6 is regulated by the results of BMP-activated Smad1/5 on the Smad6 promoter.
