MicroRNAs (miRs) are endogenously expressed 18-25-nucleotide RNAs that regulate gene expression via translational repression by binding to a goal mRNA. Recently, it was indicated that miRs act as key regulators in cell differentiation, cell development, and cell loss of life. In osteogenesis, a number of miRs (for instance miR-26a, -125b, -133, and -135) regulate osteoblast cell development or differentiation in human adipose tissue-derived stem cells, mouse mesenchymal ST2 stem cells, and mouse premyogenic C2C12 cells.
Additionally, Smad proteins management Drosha-mediated miR maturation. Therefore, miRs are intently associated to osteogenesis. Here we investigated miR expression profile by an miR array and recognized the candidate miRs, miR-141 and -200a, as pre-osteoblast differentiation-related miRs.
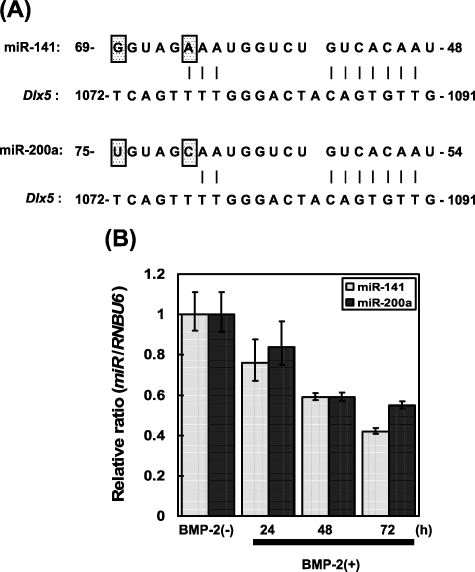
The results of miR-141 and -200a on pre-osteoblast differentiation have been examined by utilizing transfection of murine pre-osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells with mature miR-141 or -200a and antisense inhibitor for miR-141 or -200a. It was proven that miR-141 and -200a remarkably modulated the BMP-2-induced pre-osteoblast differentiation via the translational repression of Dlx5, which is a bone-generating transcription issue expressed in pre-osteoblast differentiation.
Furthermore, it was indicated that Dlx5 is a typical goal of miR-141 and -200a by utilizing a luciferase reporter assay. Thus, now we have noticed for the primary time that miR-141 and -200a are involved in pre-osteoblast differentiation in half by regulating the expression of Dlx5.
Bone morphogenetic protein 2 stimulation of tumor development includes the activation of Smad-1/5.
Morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP-2) is generally expressed in the embryo selling the event of a number of organs. Aberrant expression of BMP-2 happens in roughly 98% of lung carcinomas, nonetheless, its position in regulating tumor development is poorly understood. We present that BMP-2 induces Id-1 expression in lung most cancers cell strains via its activation of Smad-1/5, which relies on cell tradition situations. A549 cells in DMEM/5% FCS BMP-2 activated Smad-1/5 and induced a transient enhance in proliferation. In serum-free medium, BMP-2 induced considerably much less Smad-1/5 activation and Id-1 expression, and produced vital development inhibition. The have an effect on of BMP-2 on tumor development in vivo was considerably extra vital.
Recombinant BMP-2 coinjected with A549 cells, into nude mice elevated proliferation and produced a rise in Id-1 expression. Forced expression of BMP-2 in A549 cells considerably enhanced tumor development in the lungs following intravenous injection however not of subcutaneous tumors.
Tumors in the lung have been discovered to have an activated Smad-1/5 and expressed Id-1. Subcutaneous tumors expressed much less activated Smad-1/5 and Id-1 than that of controls. Human lung carcinomas have been additionally discovered to specific an activated Smad-1/5 and Id-1. We present proof that BMP-2 promotes tumor development. This paper highlights that cell tradition experiments could not reveal the complete organic impacts of BMP-2, and its exercise varies relying of the native atmosphere.
